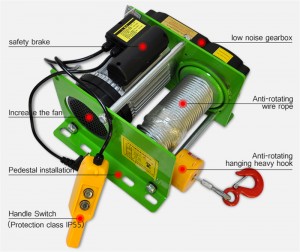
Electric hoist failures can occur due to various factors. Here are some common causes:
1. Overloading
Exceeding the hoist's rated load capacity can strain components, leading to mechanical failure.
2. Wear and Tear
Regular use can cause wear on chains, gears, and other moving parts, eventually leading to malfunction.
3. Lack of Maintenance
Infrequent inspections and inadequate lubrication can lead to rust, corrosion, and component degradation.
4. Electrical Issues
Problems with the electrical system, such as short circuits, frayed wires, or faulty controls, can cause the hoist to fail.
5. Environmental Factors
Exposure to harsh conditions, such as moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures, can affect the performance and longevity of the hoist.
6. Chain or Rope Damage
Fraying or kinking of the chain or rope can lead to failure during operation.
7. Improper Installation
Incorrect setup or alignment can lead to operational issues and increased wear on components.
8. Mechanical Obstructions
Blockages in the hoisting path or a misaligned load can cause the hoist to jam.
9. Control System Failures
Malfunctions in the control system, including limit switches and remote controls, can lead to unintended movements.
10. Overheating
Continuous use without breaks can cause the motor to overheat, leading to thermal shutdown or permanent damage.
Preventing Failures
To mitigate these issues, regular maintenance, appropriate usage training, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential. Keeping a detailed maintenance log can also help track the condition of the hoist and preemptively address potential failures.
Post time: Feb-06-2025